Advancing energy flexibility in buildings
Transforming building energy management with smart control systems
The BuildInFlexergy project, funded by the Dutch Mission-Driven Research, Development, and Innovation (MOOI) program, is revolutionizing building energy flexibility. This is supported by the Dutch Ministry of Economic Affairs and Climate Policy and the Ministry of the Interior and Kingdom Relations, and managed by the Netherlands Enterprise Agency (RVO). This four-year industry leading initiative unites 10 industry partners (including Eindhoven Engine) and 2 top universities (TU Eindhoven and TU Delft).
A unified approach to innovation
Coordinated and managed by Kropman B.V., the consortium includes installation companies, energy consultants, platform developers, building owners and managers, technology providers, and other experts. The aim is to foster open knowledge exchange and drive innovation through strategic collaboration and widespread dissemination of results.

Buildings at the heart of the energy transition
As the energy sector shifts towards a decentralized, digital, and low-carbon future, buildings—significant consumers of electricity and thermal energy—are key to providing demand-side flexibility. This flexibility allows buildings to adjust their energy use in response to external signals like electricity prices, carbon intensity, or grid constraints, without sacrificing occupant comfort or essential functions.
Kick-off meeting 17th June, 2025 | Kropman Nijmegen
The power of model predictive control
Model Predictive Control (MPC) is a cutting-edge tool for optimizing building energy performance. Unlike traditional control systems, MPC uses predictive models and real-time data to proactively manage a wide range of systems, including HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning), lighting, heat pumps, thermal storage, electric vehicles charging and other building loads It uses forecasts of occupancy, weather conditions and other relevant parameters to determine the best control actions over a future period, continuously updating the plan based on new data.
The aim of this project is to foster open knowledge exchange and drive innovation through strategic collaboration and widespread dissemination of results.

Real-time responsiveness with dynamic climate control
Dynamic climate control adjusts HVAC settings and ventilation rates based on changing indoor and outdoor conditions. This allows buildings to pre-cool or pre-heat spaces when renewable energy is plentiful or electricity prices are low, shifting loads without compromising comfort or overloading the grid.
Optimizing with key performance indicators
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are developed based on the Smart Readiness Indicator. KPIs guide decisions and balance objectives like energy cost, comfort, CO₂ emissions, and grid support. KPIs such as total energy consumption, peak load reduction, indoor comfort indices, and flexibility scores can be prioritized based on goals.
The future of building energy flexibility
The KPI-driven MPC framework makes buildings energy-efficient, grid-responsive, and climate-conscious. This approach is ideal for buildings in smart grids or demand response programs, supporting both building managers’ operational goals and energy system planners’ strategic targets.
In conclusion, combining MPC, dynamic climate control, and KPI-driven optimization can significantly enhance building energy flexibility. This strategy is crucial for making buildings active participants in the low-carbon energy system of the future.

Tackling energy challenges in buildings
The BuildInFlexergy approach
As buildings become increasingly reliant on electricity to maintain their indoor climate, they face challenges such as electricity supply and limited grid capacity.
To address these issues, Eindhoven Engine is happy to announce the BuildInFlexergy initiative commenced on May 1st, 2025.
Focus on energy flexibility
This project brings together 12 partners, including Eindhoven Engine. It aims to enhance the reliability and efficiency of local energy supply by better utilizing energy flexibility. Additionally, this initiative is particularly crucial for large, complex building systems equipped with heat pumps and thermal energy storage. These systems often experience stability and coordination issues, which can negatively impact both energy and comfort performance. Therefore, by focusing on energy flexibility, BuildInFlexergy aims to overcome these challenges and ensure a more stable and efficient energy supply for building.
Smart control systems and model predictive control
By transforming building energy management with smart control systems and model predictive control, we achieve real-time responsiveness and dynamic climate control. Moreover, this optimization uses key performance indicators. This unified approach to innovation places buildings at the heart of the energy transition, paving the way for the future of building energy flexibility.
This project not only addresses current challenges but also sets a precedent for future developments in energy-efficient building management.

“I never saw myself working at Kropman,” Shalika Walker confesses. “And honestly, I might not have hired Shalika,” Joep van der Velden admits, seated beside her. “But how the OpenCall of Eindhoven Engine changed things. We’ve now created a new position within Kropman specifically to bring Shalika on board,” says Joep with a big smile.
We are at one of the offices of Kropman. This company designs, builds, maintains, and manages building installations, including climate control. “Kropman, rooted in construction, is traditionally less dynamic compared to sectors like semiconductors or the medical industry. So, working here was not on my radar,” Shalika shares.
Kropman’s Workspace: More Than Meets the Eye
“Welcome to our living lab,” Joep announces as he leads me into a spacious, open-plan office. At first glance, it looks ordinary, with dark gray carpets, white adjustable desks, and black office chairs. Joep notices my lukewarm reaction and gives a knowing sigh, directing my attention upward. “The real innovation is actually hidden above us in the ceiling.” I follow his gaze to a beige suspended ceiling, and he points out a translucent cap. “Those are sensors. They allow us to monitor and adapt the office environment, responding to the current scenario or the presence of workers.”
At Kropman, the pride lies in being system integrators. We source pumps from one company, sensors from another, and piping and operating systems from yet another. Our goal is to seamlessly blend these components, providing our customers with a unified operating system that manages lighting, climate control, and solar panels, among other things. This integration is meticulously crafted to enhance the experience for our clients’ employees, focusing on maximal efficiency and environmental sustainability, using as little energy as possible.
Embracing Open Collaboration for Innovation
Creating an integrated system might seem straightforward, but it’s a challenging endeavor. We’re in a field dominated by heavyweights like Siemens, Honeywell, and Signify, each offering products with proprietary systems and unique data outputs, typically closed to external systems. To navigate this, we developed our software to manage and optimize the diverse systems a client might have. However, the need for a testing ground became apparent. Clients often hesitate to open their buildings for experimental setups; hence, we transformed our Breda office into a living lab.
True partnership proved elusive until we found a more receptive community in the Brainport region.
We strongly believe in an open environment for research and development. Our efforts to collaborate with universities and companies across and beyond Europe, however have been met with limited success. True partnership proved elusive until we found a more receptive community in the Brainport region. This shares a work and research philosophy similar to our own company’s, plus communication is direct and efficient, enabling us to quickly and easily connect with each other. This welcoming atmosphere was pivotal when Wim Zeiler, a former colleague now with Eindhoven University of Technology and still an advisor at Kropman, introduced us to the Eindhoven Engine OpenCall. Recognizing its potential to foster meaningful partnerships, we eagerly seized this opportunity.

Eindhoven Engine’s OpenCall: A Catalyst for Collaboration
“Working with Eindhoven Engine offers a unique experience,” Shalika explains. “We share a location with a variety of companies and students, all engaged in their own projects. This diversity is beneficial. It’s not just about casual connections, like chatting at the coffee machine; we also attend sessions to share and discuss project progress.
For instance, while working on a data prediction project, I overheard a researcher at Eindhoven Engine’s Festival of Disruption event discussing data usage in cancer research. It didn’t click immediately, but later, the idea struck me at home: we could collaborate and enhance our respective research.
These interactions open up new perspectives and inspire innovative thinking. “This collaborative atmosphere was the reason Kropman signed up for three projects in a row. One project focused on detecting and diagnosing faults in building climate systems. The second project involved personalized thermal comfort systems, allowing employees to adjust their workspace climate via a smartphone app. The third was an assessment of CO2 sensors in the market, evaluating their accuracy for reliable CO2 readings in schools.
Although these projects are completed within Eindhoven Engine, we continue to build on the research and improve the products developed.” “And that’s why we brought Shalika on board,” says Joep.
Towards automated personal comfort systems for heating, cooling and ventilation
Hello, my name is Petros Zimianitis (31 years old). I come from Greece and I was an EngD trainee in the Smart Buildings and Cities program at Eindhoven University of Technology. I studied Physics as my bachelor’s and did my master’s in Computational Physics in Greece.
Driven by my curiosity and my eagerness to come up with innovative solutions to interesting technical challenges, I started my Engineering Doctorate traineeship in 2021, to contribute to the world of the built environment.
Are we using energy efficiently?
In the Netherlands, buildings are responsible for a great proportion of the total energy consumption. It is estimated that there can be significant energy savings by improving building installations and conditioning systems. Another important issue is the reported dissatisfaction of occupants in non-residential buildings regarding their perceived comfort and air quality. This is not a very efficient way of using energy, especially now that the world is moving to more sustainable energy generation. There are also a lot of research findings regarding the differences in perceived comfort across individuals.

Individualizing comfort in offices
My project, ‘Towards automated personal comfort systems for heating, cooling and ventilation’, is part of the Brains4Buildings consortium. It aims to take the step from research towards design and, thus to develop and test a prototype personalized comfort system (PCS), controlled by a machine learning model, as a module for building management systems for office buildings. The control inputs for the system come from both objective measurements of the environmental conditions around the occupant as well as the occupants’ perceived thermal comfort and perceived air quality.
System development
The prototype PCS was developed in a real office environment, in the living lab of Kropman in Breda. Prior to now, there was been a lot of research performed in controlled experiment rooms (climate chambers) at universities and other institutes. The benefit of developing such a system in a real office environment is that the system and the interaction that the occupants have with it can be tested in real-world conditions.
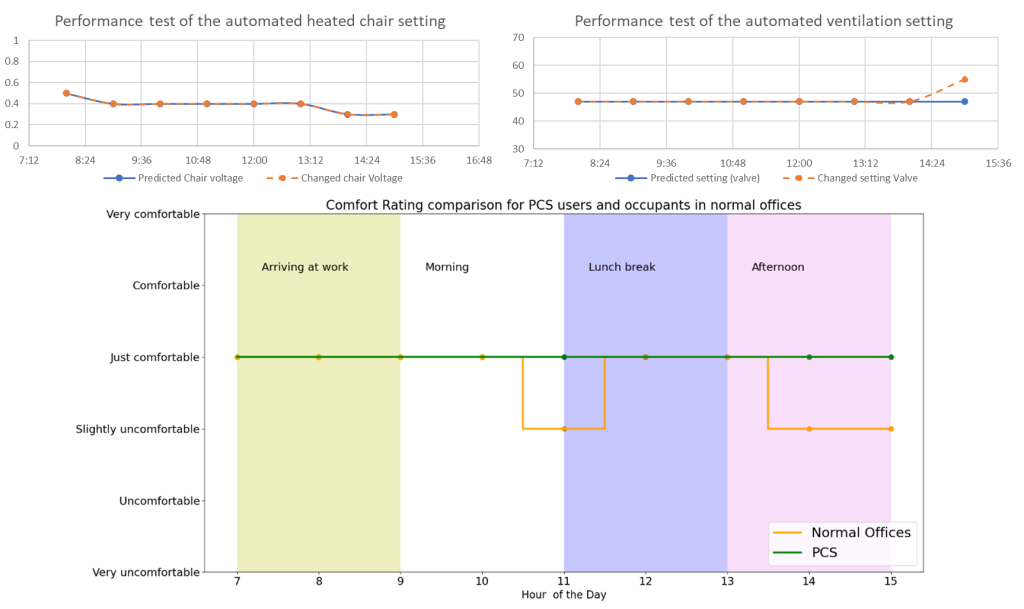
Performance
During the tests, the system showed promising performance. The machine learning models were able to predict the perfect settings for the volunteers the majority of the time. It was also reported that the volunteers that were using the PCS were felt comfortable throughout the day, whereas other people that worked in the same building in normal offices were experienced some kind of discomfort throughout the day.
What does this mean?
By individualizing comfort systems, there are huge gains that can be made in energy use. PCSs are using significantly less energy for the same task than central conditioning systems. A combination of these systems can prove to be much more energy efficient than the systems currently in use, thus, enabling buildings to easily integrate sustainable on-site energy generation solutions. All this is possible, while still providing increased levels of comfort to the occupants, which also extends to higher productivity and overall improvement of the occupants’ well-being!
By individualizing comfort systems, there are huge gains that can be made in energy use. PCSs are using significantly less energy for the same task than central conditioning systems
Improving indoor air quality in schools in the Netherlands
Hello, I’m Ayda Golahmadi, a curious individual and an EngD trainee from Iran who is always seeking fresh perspectives on everything around me. My dedication, creativity and abilities have always been directed towards fostering innovative viewpoints and adopting a holistic approach to all aspects of life. Engineering and design emerged as the perfect avenue for me to kickstart my career.
Improving indoor air quality
My research is focused on improving indoor air quality (IAQ) in schools in the Netherlands as part of the ECOS-IAQ project. The project aims to propose new strategies for improving the performance of ventilation systems in Dutch schools. The study explores the concept of ventilation effectiveness as a strategy to improve IAQ in classrooms. It demonstrates the potential of improving the effectiveness of ventilation rather than merely increasing airflow rates to meet indoor air quality needs.
Promising results
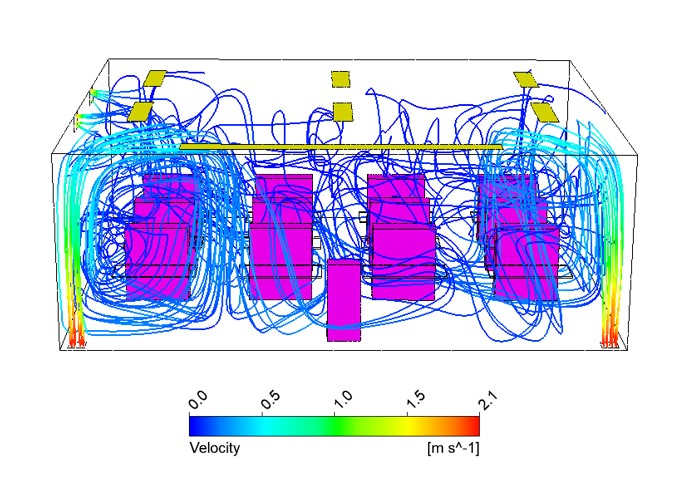
The results of my research so far have been promising. I have been able to use Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations to analyze the airflow distribution in a classroom and assess the performance of different ventilation systems. The insights gained from these simulations have been instrumental in understanding the impact of various factors on indoor air quality. One of the key findings of my research is the potential impact of implementing multi-zone ventilation concepts and methodologies in classrooms. This approach has shown promise in improving the effectiveness of ventilation and indoor air quality.
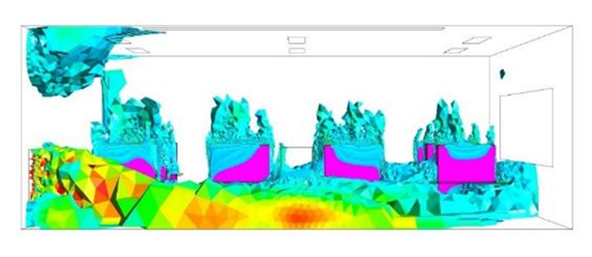
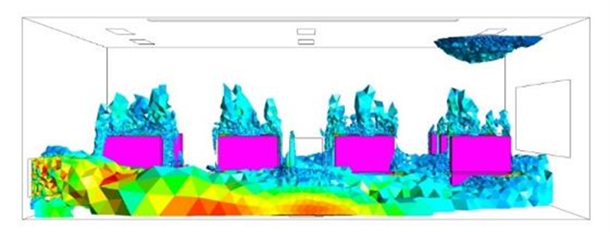
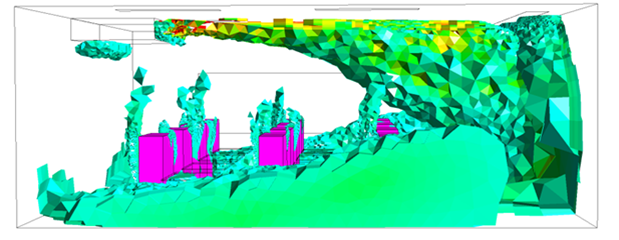
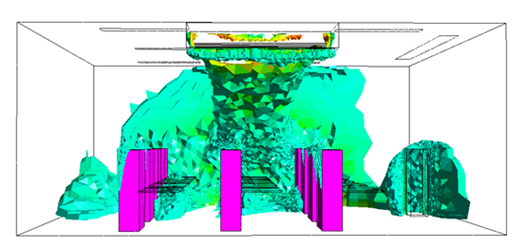
Limitations
However, there are several challenges that I still need to address. One of the main challenges is the limitations of CFD simulations. The quality of the input data has a significant impact on the accuracy of the results. Additionally, the complexity of physical phenomena such as turbulence and heat transfer can also affect the accuracy of the CFD simulations. Another challenge is the generalization of ventilation types. The study focused on two specific types of ventilation concepts: displacement ventilation and mixing ventilation. However, there are other ventilation concepts that were not considered in the study.
Impact is significant
Despite these challenges, I am optimistic about the impact of my research. Indoor air quality is a critical factor that significantly impacts the health and academic performance of students in schools. By improving the ventilation systems in schools, we can enhance the indoor air quality, leading to better health, thermal comfort and higher energy efficiency. This research addresses the social problem of poor indoor air quality in schools, which has been linked to a decrease in students’ cognitive abilities.
In conclusion, while there are challenges to overcome, the potential impact of this research is significant. The insights gained from this study will not only contribute to the academic field but also have the potential to bring about meaningful change in the real world. I look forward to continuing my work on this project and making a positive impact on the lives of students in schools.
The insights gained from this study will not only contribute to the academic field but also have the potential to bring about meaningful change in the real world.
The built environment is responsible for about 36% of the global energy demand. About 5-30% of the energy use of buildings is related to energy waste due to faults in heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems. The goal is to develop a self-learning module that can monitor and diagnose climate systems in large buildings.
Generic, robust and reliable fault detection & diagnosis tool
Rick Kramer is the leader of this project and Srinivasan is one of his PhD candidates. Srinivasan is focusing on developing a generic, robust and reliable fault detection and diagnosis tool that can help with the early detection of these faults and eliminate energy wastage.
Personalized control system in an office environment
Within this project, EngD trainee Petros is focusing on the people within large buildings. He is doing research on the control and functionality of a personalized control system that people will be able to use in their office environment to tailor it according to their needs and preferences.
More project info

From Unlikely to Unstoppable: Embracing Diversity in the Building Industry

In full speed with students and young professionals
Videos
The built environment is responsible for about 36% of the global energy demand. About 5-30% of the energy use of buildings is related to energy waste due to faults in heating, ventilation and air-conditioning systems. The goal is to develop a self-learning module that can monitor and diagnose climate systems in large buildings.
Rick Kramer – Project leader & Assistent Professor TU/e | Srinivasan Gopalan – PhD canditate TU/e
The goal is to develop a self-learning module that can monitor and diagnose climate systems in large buildings. Rick Kramer is the project leader of this project. Srinivasan is one of his PhD candidates who is focusing on developing a generic, robust and reliable fault detection and diagnosis tool
Petros Zimianitis – EngD trainee TU/e
Petros is focusing on the people within large buildings. He is doing research on the control and the functionality of a personalized control system, that people will be able to use in their office environment to tailor it according to their needs and preferences.