My research is focused on using transcranial electric stimulation for epilepsy patients that cannot be treated using medicine or surgery and is part of the PerStim project. This project was conceived from the wish to be able to reduce the treatment gap in epilepsy and thus lower the burden of this disease on the patients and society.
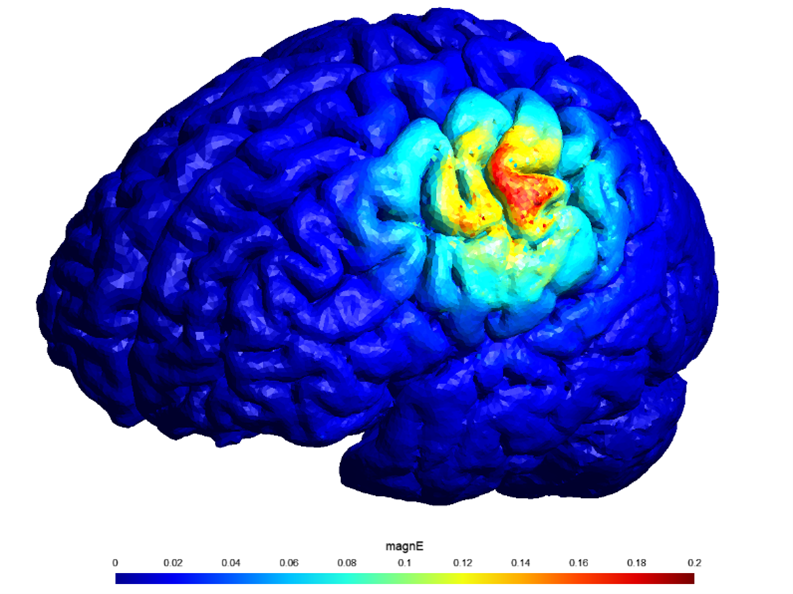
Electrical stimulation is simple, but very complex
Together with the Ghent University Hospital, Kempenhaeghe and Philips we started to research the use of electrical stimulation for epilepsy treatments. Through extensive literature studies, we found that the working mechanism of this technology is still poorly understood. Thus, we set out to answer a fundamental question using clinical studies: “Are we stimulating the brain with currents that go straight through the skull, or is it taking a more complicated route like the facial nerves?”
This method holds great promise for the future because of its affordability, simplicity, and potential for home use, which could ultimately reduce the need for frequent hospital visits.
To support these studies, I was tasked with making patient models, optimizing the electrode positions as well as analyzing the data. Together with students from Fontys and the TU/e, we built a full workflow to do this in a very quick and efficient manner. Eindhoven Engine enabled us to cooperate with the students from the Fontys. Their working mentality and different way of approaching problems were fundamental to significant parts of this work. Our clinical studies are still running, but preliminary results have shown that the answer to the abovementioned question might be that the stimulation works via both the direct and the indirect paths.

Looking into the future
Even though the use of transcranial electric stimulation is more complex than initially assumed, we have just started to unravel the actual working mechanism and I wholeheartedly believe that as we gain a deeper understanding, we can improve the methods and their efficacy. This method holds great promise for the future because of its affordability, simplicity, and potential for home use, which could ultimately reduce the need for frequent hospital visits.
My time at the university is running out, but I am still as fascinated by the world of brain stimulation as I was when starting this project and I’ll keep working in this field to improve the understanding of these techniques and unlock their potential for patients.
