About the project
The need to reduce CO2 emissions makes energy in the built environment a key issue given that inefficient buildings represent around 35% of the total energy consumption. Continuous Monitoring (CM) and Fault Detection and Diagnosis (FDD) are complex but important technologies in detecting inefficiencies in Heating Ventilation Air Conditioning (HVAC). With a rise in demand for cooling caused by global warming, this project is developing a new approach based on data analytics and machine learning. This will enable resulting CM and FDD modules to be programmed in a state-of-the-art Building Management System (BMS) and become market-ready by the end of the project.
About the project
Installations in buildings are responsible for around 35% of all energy consumption, approximately 20% of which is due to inefficient operations. Inferior environmental conditions within classrooms can have both short- and long-term health effects, mainly due to the presence of particulate matter. With greater insights into sensors, data interpretation, trend signaling, continuous monitoring, fault detection/diagnosis and predictive maintenance, problems can be identified in the Heating Ventilation Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems of schools. The ECoS-IAQ project focuses on the creation of product development concepts for air handling manufacturers, air filter manufacturers, control companies and installers.
Infographic

About the project
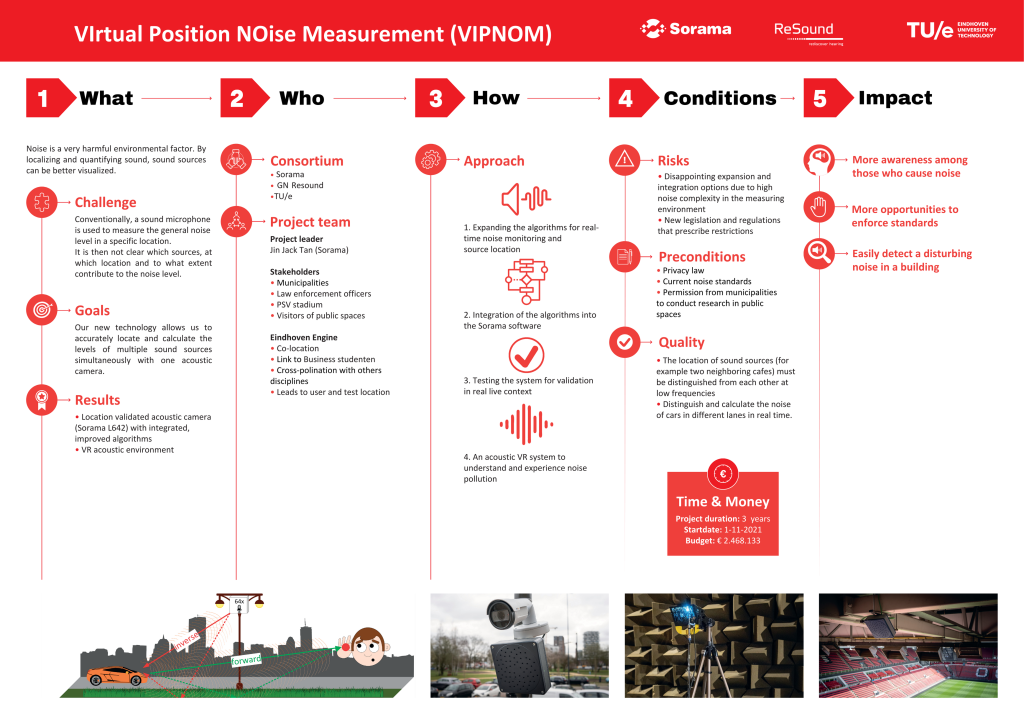
VIPNOM focuses on the development of advanced noise measurement method and experiencing noise in acoustic virtual reality. Noise is the second largest harmful environmental factor in Europe and claims a million healthy years of life each year due to stress and sleep disturbances. To effectively combat unwanted noise, it is important to first be able to measure it.
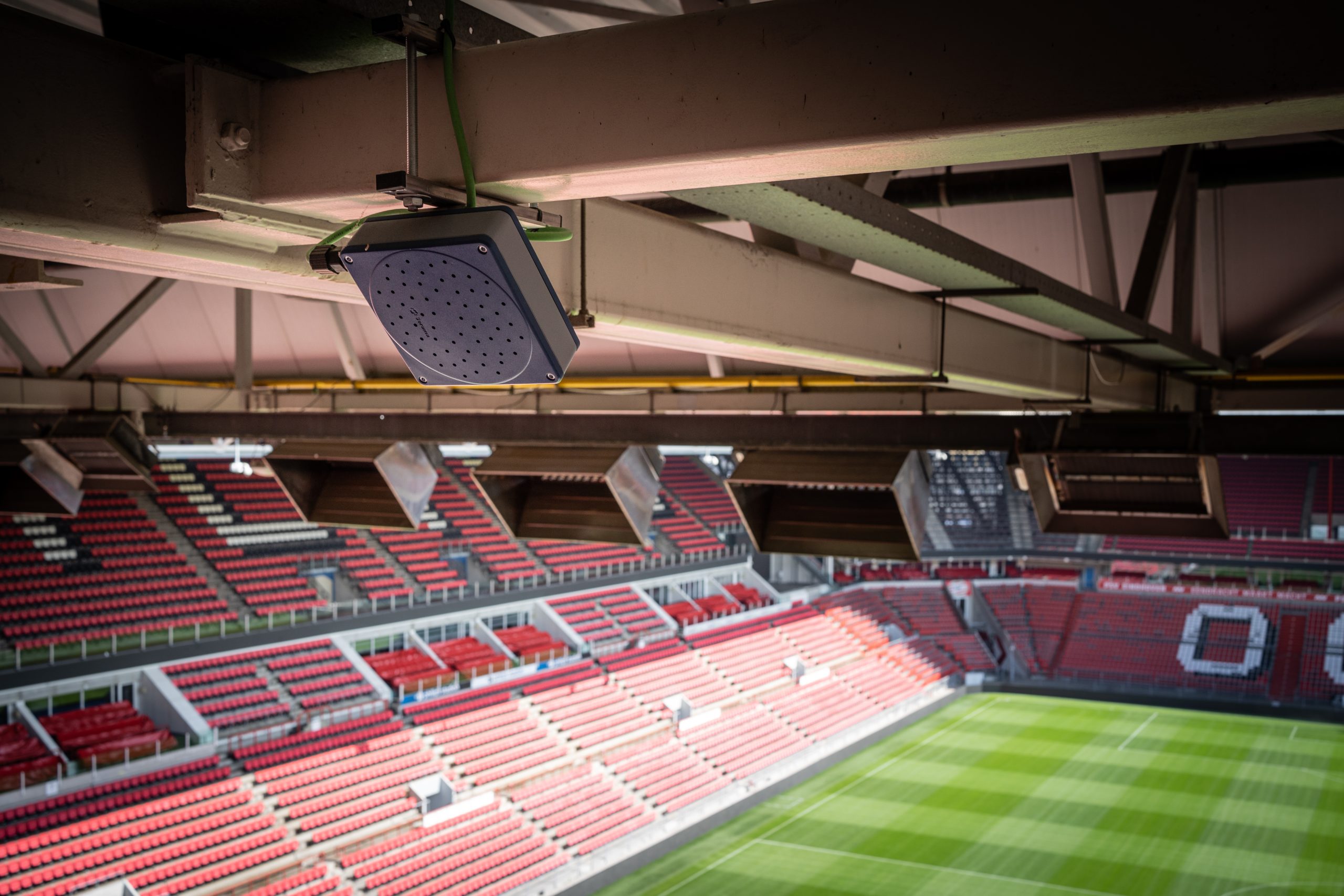
Currently, noise is measured by placing microphones at specific locations and measurements made are applicable on those exact locations. VIPNOM advocates the use of microphone arrays at central locations, where noise levels at several other locations can also be measured simultaneously, such as at the balconies of an apartment building next to a noisy road, or across a large area of the city centre. In order to accurately measure noise levels, VIPNOM will further develop, optimize and implement the methods that are developed in the base project (ZERO). The resulting algorithms will be tested in the living labs Stratumseind and Strijp-S. Additionally, the same technique will also be applied in an acoustic virtual reality to allow interested parties (such as citizens and policy officers) to auralise and experience noise beyond just decibel values on a written report.
Infographic
Assignment for HBO/WO student

Spatial calibration of acoustic cameras for smart cities and stadiums
More project info
Jin Jack Tan – Project leader
Patrick Wijnings – Systems Engineer
Brains4 Buildings
The goal is to develop a self-learning module that can monitor and diagnose climate systems in large buildings.
About the project
The goal is to develop a self-learning module that can monitor and diagnose climate systems in large buildings. This will enable a climate system to perform better; for instance, lower energy consumption, better thermal comfort and better air quality. More efficient maintenance is also possible. The module will be used as an add-on for the Building Energy Management System (BEMS) of offices.
More about the project
Rick Kramer – Project leader & Srinivasan Gopalan – PhD canditate
Petros Zimianitis – EngD trainee
About the project
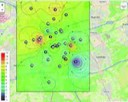
The concentration of nitrogen dioxide and particulate matter is still too high in the Netherlands according to WHO guideline values in 2021. In the Eindhoven region, several technical developments and research and innovation initiatives have been started in this field. As a result, a lot of information on population dynamics, such as commuting traffic and air pollution, is readily available. In DynaPopeX, this information is brought together for the first time and visualization techniques can be used to make connections to the sources of air pollution.
The combination of data, location and human movements in Eindhoven makes it possible to take tangible measures to reduce the exposure of people on the street to harmful particulate matter and limit possible harm to health.